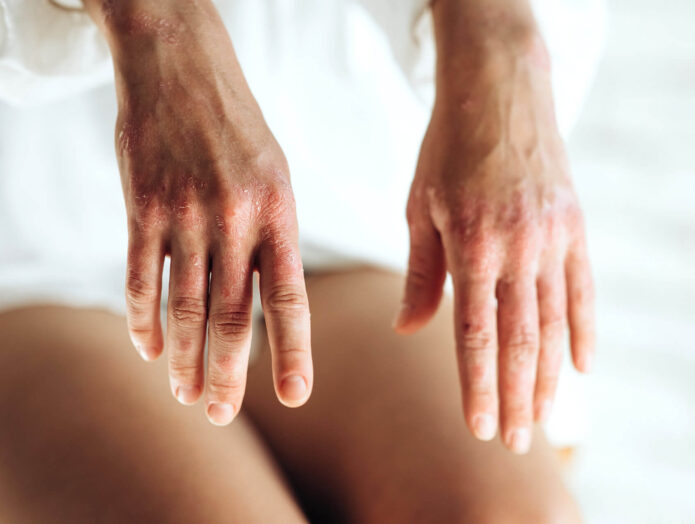
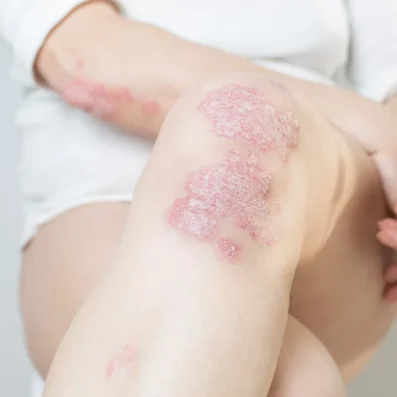
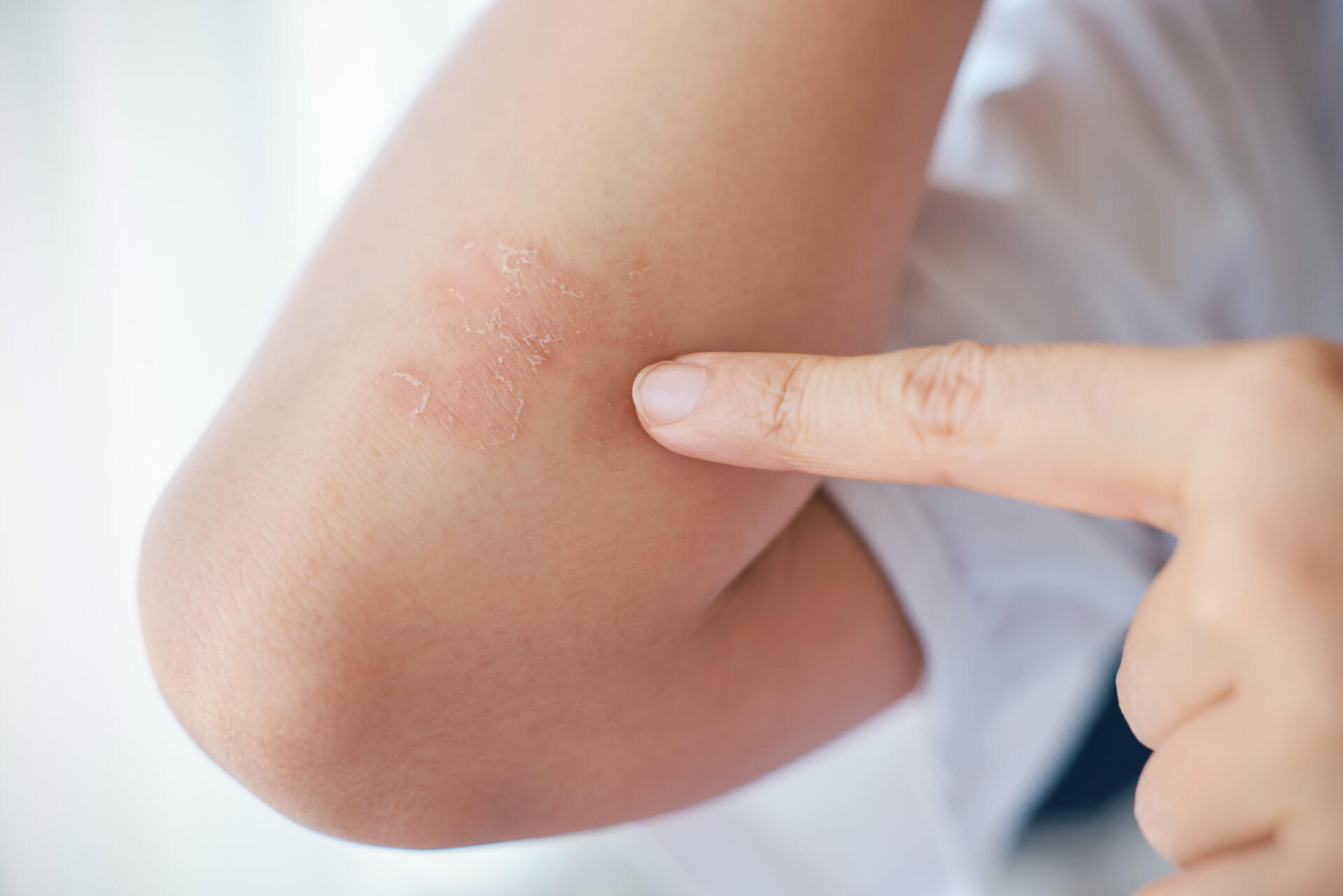
What Causes Psoriasis?
The cause of this typically life-long disorder is not fully understood, but genetics, environmental factors and the immune system are thought to play a role in its development.
Treatment Options for Psoriasis
A variety of treatments, including topicals and systemic therapies, can be used to clear up the skin once it manifests. Our AboutSkin physicians also offer the latest biologics (biological drugs) by injection to help treat psoriasis.
Biologics: A Targeted Approach to Psoriasis Treatment
Biologics are a relatively newer class of medications that target specific parts of the immune system involved in psoriasis. These treatments work from within the body to reduce inflammation and slow down the overproduction of skin cells. Unlike traditional systemic treatments, biologics are designed to block certain proteins or cells that play a role in the development of psoriasis, such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) or interleukins.
Biologics can be administered in different ways depending on the medication. Some are injected under the skin, others are given through an intravenous (IV) infusion and a few are available as oral medications.
Benefits of Biologics for Psoriasis:
- Targeted treatment: Biologics specifically target the immune system components responsible for psoriasis, offering a more focused approach compared to traditional treatments.
- Effective for moderate to severe psoriasis: For those who haven’t responded well to topical treatments or phototherapy, biologics can offer significant improvement in symptoms.
- Convenient dosing: Depending on the biologic, injections may be required as infrequently as once every few weeks or months, making it a convenient option for long-term management.
Common biologics used for psoriasis include:
- Adalimumab
- Ustekinumab
- Secukinumab
- Ixekizumab
While biologics can be highly effective, it’s essential to consult with a Board-Certified Dermatologist to determine if this treatment is appropriate for you. Biologics may suppress parts of the immune system, so they are typically recommended for individuals with moderate to severe psoriasis.
Topical Medications: Managing Psoriasis on the Surface
Topical medications are often the first line of treatment for mild to moderate psoriasis. These treatments, applied directly to the skin, can help reduce inflammation, slow down cell turnover and relieve discomfort. Topicals come in various forms, such as ointments, creams, gels and shampoos.
Common Types of Topical Psoriasis Medications
- Corticosteroids: These anti-inflammatory medications are the most frequently prescribed treatment for psoriasis. They reduce inflammation and slow the growth of skin cells. Corticosteroids are available in varying strengths, from mild to potent, and are usually applied once or twice a day.
- Vitamin D analogues: Synthetic forms of vitamin D, such as calcipotriene, help slow down the skin cell production that contributes to psoriasis plaques. They are often used in combination with corticosteroids for better results.
- Retinoids: Topical retinoids, a form of vitamin A, can help normalize skin cell turnover rates and reduce scaling and redness. Tazarotene is a common topical retinoid used for psoriasis.
- Calcineurin inhibitors: These medications, such as tacrolimus and pimecrolimus, are used to reduce inflammation and immune response. They are often recommended for sensitive areas like the face or skin folds.
- Salicylic acid: Often found in over-the-counter products, salicylic acid helps remove scales and reduce thick plaques.
- Coal tar: An older but effective treatment, coal tar helps reduce scaling, itching and inflammation. It’s available in various strengths and can be applied as a cream, shampoo or ointment.